آنژیوگرافی چیست ؟
آنژیوگرافی : بیماری های قلب و عروق از شایع ترین بیماری های قرن حاضر محسوب شده و نارسایی قلبی بزرگترین عامل مرگ و میر در
جوامع صنعتی و نیمه صنعتی به حساب می آید.
به دلیل اهمیت این موضوع،ابزارها و روش های مختلفی به منظور بررسی عملکرد قلب در پزشکی نوین ابداع شده که از جمله آنها می توان به
آنژیوگرافی به کمک تصویربرداری اشعه ایکس اشاره نمود.
از نظر لغوی آنژیوگرافی از دو واژه آنژیو به معنای رگ و گرافی به معنای نگاشتن تشکیل شده است.هدف این روش دستیابی به محدوده ی
گسترده ای از اطلاعات ساختاری (Structural) و عملکردی (Functional) در رابطه با قلب و سیستم گردش خون است،به طوری که نه تنها در
تشخیص نوع بیماری قلبی به پزشک یاری برساند،بلکه امکان پیش بینی نارسایی قلبی احتمالی در آینده و پیشگیری ازآن را نیز فراهم آورد.
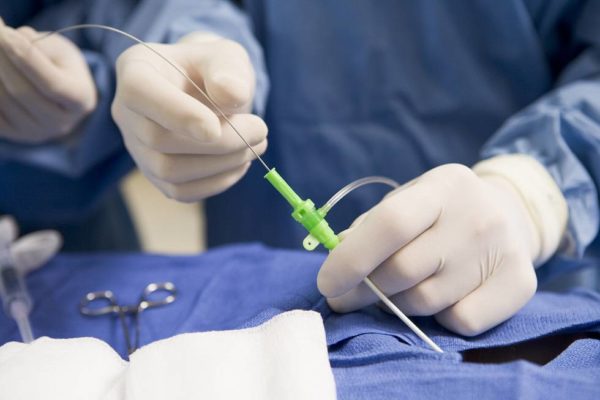
عکس بردازی از قلب
نحوه ی عملکرد
در آنژیوگرافی یک کاتتر پلاستیکی نازک به داخل یک رگ بزرگ سطحی (نظیر شریان فمورال،شریان براکیال،ورید جوگولر) وارد می شود و به
سمت ناحیه هدف هدایت می شود.
سپس ماده ی حاجت ید دار به داخل رگ تزریق می شود( برای بیمارانی که به مواد ید دار حساسیت دارند می توان از گاز دی اکسید کربن
استفاده کرد) سپس پرتوهای ایکس از قسمت بالایی دستگاه فلوروسکوپی به سمت ناحیه ی هدف تابانده می شود و گیرنده هایی در قسمت
پایین دستگاه وجود دارد که این پرتوهارا جذب می کند.
پس از این فرایند، تصویری واضح و دقیق از رگ و قسمت های مختلف آن بر روی عکس یا فیلم ظاهر می شود.
در هنگام عکس برداری به علت اینکه بافت عروقی بدن جزء نسج نرم بوده و تراکم کمی دارد بنابراین اشعه به راحتی از همه ی آن ها عبور
کرده و بر روی فیلم نمی توان هیچ تصویری داشت.
روش انجام آنژیوگرافی چگونه است؟
متخصص آنژیوگرافی پس از شروع آنژیوگرافی قلب، شما به پشت روی تخت آنژیوگرافی دراز می کشید. ممکن است به درو بدن و پای شما
یک کمربند بسته شود. دوربین اشعه ایکس به دور سینه و سر شما چرخیده و از زوایای گوناگون عکس می گیرد.
محل ورود کاتتر که بر روی دست و یا کشاله ران است، توسط محلول های ضد عفونی تمیز شده و حجم کمی ماده بی حس کننده در آن تزریق
می شود.
ممکن است بریدگی کوچکی توسط پزشک در این منطقه ایجاد شود. سپس توسط پرستار از شما یک لاین وریدی (رگ) گرفته می شود.
ممکن است یک داروی آرامش بخش از طریق ورید به شما تزریق شود تا باعث آرامشتان گردد. از این طریق داروها و مایع نیز به شما تزریق
می شود. حال یک لوله پلاستیکی کوچک (شیت) داخل شریان شما قرار داده می شود.
یک کاتتر یا لوله بلند از داخل این شیت عبور کرده و به سمت قلب هدایت می شود. عبور کاتتر نباید باعث درد شود. اگر احساس درد می کنید،
پزشک خود را آگاه سازید.
از داخل کاتتر ماده حاجب به داخل عروق کرونر تزریق می شود. هنگام تزریق ممکن است شما احساس گرما یا گر گرفتگی داشته باشید. ولی
هر نوع احساس درد یا سنگینی را به پزشک اعلان نمایید.
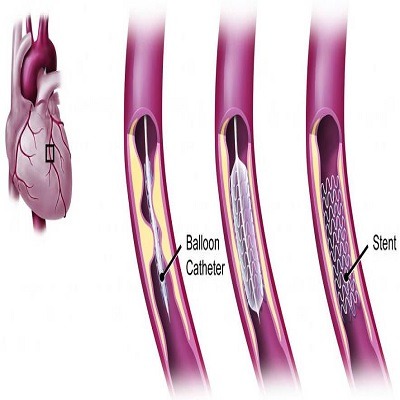
آنژیوگرافی
ماده حاجب
ماده حاجب بخوبی توسط دوربین اشعه ایکس مشاهده می شود به راحتی پزشک را قادر می سازد تا چنانچه گرفتگی و تنگی در رگ های
قلب وجود داشته باشد، آن را تشخیص دهد.
بر اساس آنچه پزشک در آنژیوگرافی شما مشاهده می کند، ممکن است تصمیم بگیرد اقدامات دیگری از جمله باز کردن رگ به کمک
آنژیوپلاستی را انجام دهد.
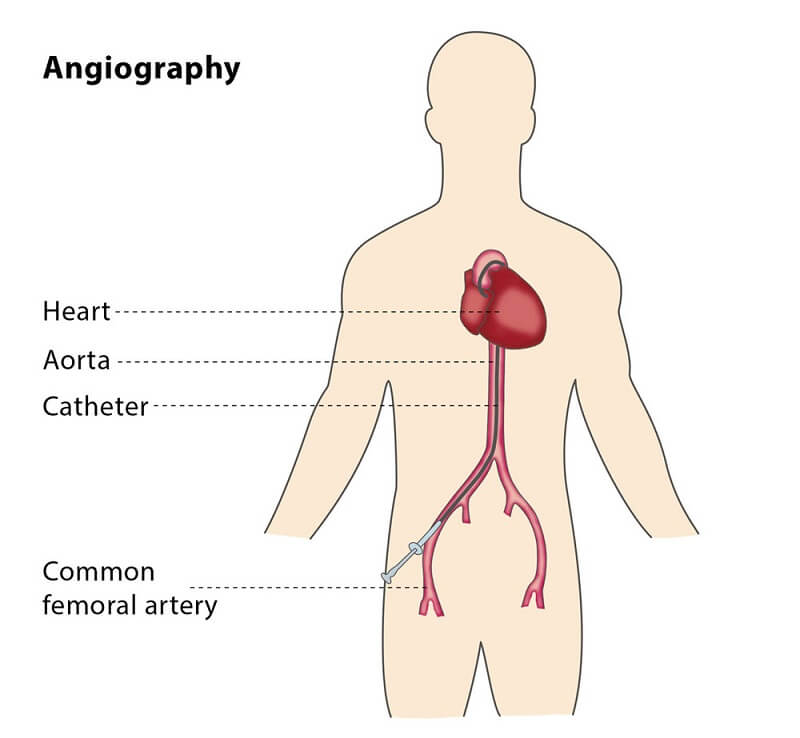
آنژیوگرافی
در حین انجام آنژیوگرافی قلب ممکن است از شما چند کار خواسته شود به عنوان مثال: نفس عمیق بکشید، نفس خود را نگه دارید، سرفه
کنید و یا موقعیت دست خود را تغییر دهید.
در زمان آنژیو، الکترودهای روی سینه برای ثبت نوار قلب به شما وصل هستند. همچنین ممکن است مواد ضد انعقاد (آنتی کواگولانت) برای
اجتناب از انعقاد خون به شما تزریق گردد.
بیمار هنگام آنژیوگرافی هوشیار بوده و تمام مراحل را می تواند مشاهده نماید. انجام آنژیوگرافی حدود یک ساعت طول می کشد که شامل
مراحل قبل و بعد از آن نیز می باشد.
مراقبت های بعد از آنژیوگرافی چیست؟
✅ در آنژیوگرافی پس از انتقال بیمار به بخش آنژیوگرافی بدون انجام بیهوشی و با بی حسی موضعی عکسبرداری از عروق قلب انجام می
گیرد.
✅ پس از اتمام، چنانچه آنژیوگرافی عروق از طریق کشاله ران انجام گرفته باشد بیمار حدود ۶ ساعت بی حرکت مانده و بواسطه گذاشتن
کیسه شن خونریزی کنترل می شود.
✅ در صورت انجام آنژیوگرافی قلب از طریق شریان دست (رادیال) بلافاصله مریض اجازه دارد بدون محدودیت حرکت کرده و نیازمند استراحت
نمی باشد، اما حدود ۴ ساعت تحت نظر خواهد بود.
✅ آنژیوگرافی تنها یک روش تشخیصی است اما چنانچه لازم باشد می توان پس از تصمیم گیری، باز کردن عروق دچارگرفتگی را آغاز کرد
(آنژیوپلاستی)
هزینه آنژیوگرافی درحدود چقدر است ؟ در سال 98
در طیف دیگر اگر طرح سلامت فعلی ادامه یابد در بیمارستان های دولتی مانند حضرت رسول، مدرس، مرکز قلب تهران امیر آباد کارگر شمالی و
بیمارستان قلب شهید رجائی هزینه ی آنژیوگرافی حدود پانصد هزار تومان و هزینه آنژیوپلاستی یا همان هزینه بالن قلب بطور متوسط ۱ تا ۳
میلیون تومان می باشد.
در بیمارستان شهید مصطفی خمینی نیز آنژیوگرافی و آنژیوپلاستی تحت پوشش بیمه انجام می گیرد که در صورت داشتن بیمه تکمیلی
هزینه آنژیوگرافی و نیز هزینه آنژیوپلاستی برای بیمار کاملا رایگان خواهد بود.
در تصویر زیر بیمه های تحت پوشش بیمارستان شهید مصطفی خمینی ذکر شده است:
هزینه آنژیوگرافی
بیماران تامین اجتماعی
بیماران تامین اجتماعی می توانند با مراجعه به بیمارستان میلاد یا شهید لواسانی بطور رایگان تحت آنژیوگرافی قرار گیرند، این بیماران چنانچه
لازم باشد که تحتآنژیوپلاستی قرار گیرند در شورای استنت مطرح شده و در صورت پذیرش بطور رایگان آنژیوپلاستی انجام خواهد گرفت.
بیمارانی که تحت پوشش بیمه های تکمیلی هستند اغلب به ۲ گونه هزینه هایشان پرداخت می شود یا بطور نقدی با بیمارستان حساب کرده و
با مدارک جهتدریافت هزینه به بیمه خود مراجعه می نمایند؛ اما راحت تر است که یک معرفی نامه جهت انجام آنژیوگرافی یا آنژیوپلاستی و یا هر
دو از بیمه تکمیلی خود گرفته و بهبیمارستان تحویل دهند.
اغلب بیمه های تکمیلی هزینه آنژیوگرافی را به طور کامل و بخشی یا تمام هزینه های آنژیوپلاستی را متقبل می شوند.
angiography
History
The technique was first developed in 1927 by the Portuguese physician and neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon to provide
contrasted x-ray cerebral angiography in order to diagnose several kinds of nervous diseases, such as tumors, artery disease and arteriovenous
malformations.
Moniz is recognized as the pioneer in this field. He performed the first cerebral angiogram in Lisbon in 1927, and Reynaldo dos
Santos performed the first aortogram in the same city in 1929. In fact, many current angiography techniques were developed by the Portuguese
at the University of Lisbon. For example, in 1932, Lopo de Carvalho performed the first pulmonary angiogram via venous puncture of the superior
member; in 1948 the first cavogram was performed by Sousa Pereira. Radial access technique for angiography can be traced back to 1953, where
Eduardo Pereirafirst cannulated the radial artery to perform a coronary angiogram. With the introduction of the Seldinger technique in 1953, the
procedure became markedly safer as no sharp introductory devices needed to remain inside the vascular lumen.
What is an angiogram?
An angiogram uses X-rays and a special dye (contrast) to take pictures of the arteries in your brain, heart, and kidneys.
The dye is injected into a small tube or catheter into an artery in your groin or (sometimes) your arm. The small tube is inserted after an injection of local anaesthetic around the artery. Sometimes intravenous sedation is given. After the dye is injected, pictures are taken using an X-ray machine.
Benefits associated with an angiogram
-
Used for diagnosis to show very detailed pictures of the arteries inside your brain, heart and kidneys
-
Can be used to show blockages in your arteries
Risks associated with an angiogram
Your doctor knows the risks of having an angiogram. Your doctor will consider the risks before recommending you to have an angiogram. Possible risks are:
-
Often not recommended in early pregnancy
-
Small amount of radiation. The amount of radiation you are exposed to depends on the number of pictures taken and the part of the body being examined
-
Extremely small chance you could develop cancer in the long term from the radiation
-
If you are taking some medications. These include anticoagulants (blood thinning medications) and diabetic medication
-
If you have a known kidney disease
-
An allergic reaction from the dye. You may have nausea, sneezing, vomiting, itching, hives and dizziness. More serious reactions can occur, but are very rare
-
Infection, bleeding or injury at the site of an injection
-
Blood clot in the wall of the blood vessel or a weakness of the blood vessel wall that may need treatment
If you are at all concerned regarding the risks, talk to your doctor before the examination.
Preparation for an angiogram
You will usually be admitted to hospital as a day patient for this procedure.
-
Bring your referral letter or request form and all X-rays taken in the last 2 years with you
-
Leave the X-rays with the radiology staff as the doctor may need to look at them. The radiology staff will tell you when these are ready to be picked up
-
Wear comfortable, loose clothing
-
Leave all jewellery and valuables at home
-
You may be asked not to eat for four hours before the angiogram
-
You will be allowed to drink clear fluids such as black tea, coffee, clear soup or water during the four hours before the Angiogram. It is important for your kidneys to have fluids
Important to tell your doctor before the scan
-
If you are or may be pregnant
-
If you have any allergies and medical conditions, including asthma, diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease or thyroid problems
-
About any medications you are taking
Just before the angiogram
-
You may be given a gown to wear
-
You may be asked to remove any metal objects
-
You will need to have a needle put into the back of your hand if you are having sedation during the procedure Consent
You have the right to refuse an examination and may do so if you wish. You may be asked to complete a consent form.
What happens during an angiogram?
You will be asked to lie flat on your back on the X-ray bed. Staff will place sterile drapes over you.
Staff will put a small tube or catheter into an artery in your arm or groin and inject the dye into it.
Possible side effects of ‘dye’:
-
You may feel a slight coolness and a flushing for a few seconds
-
Part of your body may feel warm. If this bothers you, tell the staff
Once you are ready, the X-ray staff will go behind a screen or into the next room to start the X-ray machine. They will ask you to be still, and may ask you to take a deep breath and hold your breath during the X-rays.
When your X-ray is finished you will be asked to wait while the X-ray staff check the pictures, as you may need another X-ray.
The test including getting you ready usually takes between 30 minutes to one hour.
When will I get the results?
The amount of time it takes for you to get your results will differ depending on where you get your scans done. The radiology doctor will look at the pictures and write a report. The pictures may be on films or on a CD.
Ask whether you should wait to take the pictures and report with you, or whether they will be sent to your doctor.
Your doctor will need to discuss the report with you. You will need to make an appointment to do this.
After the procedure
After the procedure staff will check your groin or arm, and your pulse and blood pressure for 4 to 6 hours. You may need to stay in hospital over night and will usually need to rest for 24 hours before returning to normal activities.
-
Staff will need to take out the needle if it is still in your groin or arm
-
Staff will give you any special instructions
-
The dye will pass out of your body in your urine. You will not notice it as it is colourless
-
Drink plenty of fluid to help get rid of the dye
If you had a sedative
-
You must not drive a car or take public transport and must have someone with you for 24 hours afterwards
-
You must not operate machinery for the rest of the day
Costs
For an Australian patient in a Public Hospital in Western Australia
-
Public patient – no cost to you unless advised otherwise
-
Private patient – costs can be claimed through Medicare and your health insurance provider
For a patient in a Private Hospital or Private Imaging Site in Western Australia or a patient outside Western Australia
-
Ask your doctor or the staff where you are having your test done what the cost will be

