دستگاه پالس اکسی متر(Pulse Oximetery)
پالس اکسی متر : در بدن انسان به طور مداوم فعالیت های متابولیک برای ادامه حیات صورت می گیرد.فعالیت متابولیک با مصرف اکسیژن و تولید دی اکسید کربن و انرژی همراه است.بدون وجود اکسیژن تولید انرژی ناچیز است(متابولیسم بی هوازی)،به علاوه در متابولیسم بی هوازی اسید لاکتیک تولید می شود،که می تواند در تعادل اسید و باز بدن اختلال ایجاد کند.
برای انجام اعمال متابولیک و برای حفظ حیات،باید اکسیژن از هوا به ریه ها و سپس به داخل خون وارد شود و توسط جریان خون به بافت ها برسد.در نتیجه اطلاع از میزان اکسیژن خون یکی از پارامترهای حیاتی در تشخیص و درمان بسیاری از بیماری ها و آسیب های بافتی است.
پالس اکسی متر
مکانیسم انتقال اکسیژن در بدن
سیستم انتقال اکسیژن در بدن از چهارقسمت اصلی تشکیل شده است:
- ریه ها
- قلب
- رگ های خونی
- بافت های مصرف کننده
پارامترهایی که معمولا برای اندازه گیری میزان اکسیژن خون استفاده می شود عبارتند از:
الف) فشار جزئی اکسیژن خون(PO2)
ب) درصد اشباع اکسیژن خون(SO2)
سیستم های اندازه گیری میزان اکسیژن خون
- آنالیزورهای گازهای خون
- Co اکسی متر
- پالس اکسی متر
پالس اکسی متر
اصول پالس اکسی متر
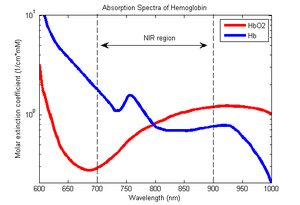
رایج ترین شیوه اندازه گیری درصد اشباع اکسیژن خون تکنیک نوری است، که از خواص نوری خون جهت محاسبه درصد اشباع اکسیژن خون استفاده می شود،به رنگ قرمز درآمده و زمانی که اکسیژن آن مصرف می شود، به رنگ آبی تیره در می آید.این ویژگی نشانگر تغییر میزان جذب نور در اثر تغییر میزان اکسیژن است.
اجزای دستگاه پالس اکسی متر
الف) پروب
ب) مدارات کنترلی
ج) نمایشگرLCD
کاربردهای پالس اکسی متری
- اتاق عمل
- fخش های مراقبت ویژه(CCU,ICU)
- اتاق CPR
- در هنگام استفاده از دستگاه ونتیلاتور
- در بخش مراقبت ویژه نوزادان(NICU)
عواملی که میتواند موجب اختلال در ثبت نتیجه شوند
لاک ناخن، اختلالات عروقی، کسانی که فشار خون بالا یا پایینی دارند، دمای غیرعادی بافت، مستقیم تابیدن نور خورشید به پروب، سفت بستن پانسمان و محکم قرار دادن پروب بر روی عضو، درصورتی که مریض فیستول وریدی داشته باشد، فرد انمی داشته باشد.
شیوهٔ عملکردی
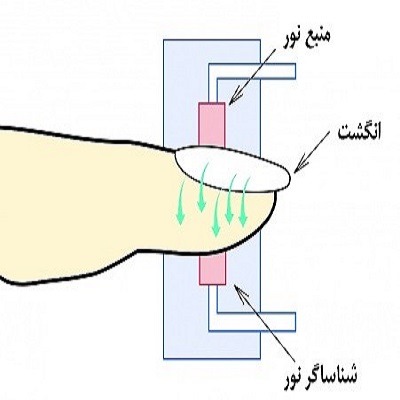
پروب دستگاه را بر روی انگشت سبابه، شست پا، نوک بینی و نرمهٔ گوش قرار میدهیم، بر روی قسمت بالایی پروب یک دیود منتشر کنندهٔ نور وجود دارد که دو نور قرمز و مادون قرمز را منتشر میکند، نور از میان بافتها عبور نموده (بافت بین پروب) و یک گیرندهٔ نوری آن را دریافت میکند و شریان را عبور میکند. نور قرمز توسط هموگلوبین و نور مادون قرمز توسط اکسی هموگلوبین جذب میشود،
سپس این اطلاعات به خود دستگاه منتقل میشود و آنجا با یک محاسبهٔ لگاریتمی میزان اشباع هموگلوبین با اکسیژن مشخص میگردد.
در واقع اين دستگاه ميزان اکسيژن را به عنوان درصدی از مولکولهای هموگلوبين که با اکسيژن آميخته شدهاند را نسبت به ميزان کل مولکولهای هموگلوبين اندازهگيری می کند.
Function
A blood-oxygen monitor displays the percentage of blood that is loaded with oxygen. More specifically, it measures what percentage of hemoglobin, the protein in blood that carries oxygen, is loaded. Acceptable normal ranges for patients without pulmonary pathology are from 95 to 99 percent. For a patient breathing room air at or near sea level, an estimate of arterial pO2 can be made from the blood-oxygen monitor “saturation of peripheral oxygen” (SpO2) reading.
A typical pulse oximeter uses an electronic processor and a pair of small light-emitting diodes (LEDs) facing a photodiode through a translucent part of the patient’s body, usually a fingertip or an earlobe. One LED is red, with wavelength of 660 nm, and the other is infrared with a wavelength of 940 nm. Absorption of light at these wavelengths differs significantly between blood loaded with oxygen and blood lacking oxygen.
Oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more infrared light and allows more red light to pass through. Deoxygenated hemoglobin allows more infrared light to pass through and absorbs more red light. The LEDs sequence through their cycle of one on, then the other, then both off about thirty times per second which allows the photodiode to respond to the red and infrared light separately and also adjust for the ambient light baseline.
پالس اکسی متر
Advantages
Pulse oximetry is particularly convenient for noninvasive continuous measurement of blood oxygen saturation. In contrast, blood gas levels must otherwise be determined in a laboratory on a drawn blood sample.
Pulse oximetry is useful in any setting where a patient’s oxygenation is unstable, including intensive care, operating, recovery, emergency and hospital ward settings, pilots in unpressurized aircraft, for assessment of any patient’s oxygenation, and determining the effectiveness of or need for supplemental oxygen.
Although a pulse oximeter is used to monitor oxygenation, it cannot determine the metabolism of oxygen, or the amount of oxygen being used by a patient.
For this purpose, it is necessary to also measure carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. It is possible that it can also be used to detect abnormalities in ventilation. However, the use of a pulse oximeter to detect hypoventilation is impaired with the use of supplemental oxygen, as it is only when patients breathe room air that abnormalities in respiratory function can be detected reliably with its use.
Therefore, the routine administration of supplemental oxygen may be unwarranted if the patient is able to maintain adequate oxygenation in room air, since it can result in hypoventilation going undetected.
Limitations
Pulse oximetry solely measures hemoglobin saturation, not ventilation and is not a complete measure of respiratory sufficiency. It is not a substitute for blood gases checked in a laboratory, because it gives no indication of base deficit, carbon dioxide levels, blood pH, or bicarbonate (HCO3−) concentration.
The metabolism of oxygen can be readily measured by monitoring expired CO2, but saturation figures give no information about blood oxygen content. Most of the oxygen in the blood is carried by hemoglobin; in severe anemia, the blood contains less hemoglobin, which despite being saturated cannot carry as much oxygen.
Erroneously low readings may be caused by hypoperfusion of the extremity being used for monitoring (often due to a limb being cold, or from vasoconstriction secondary to the use of vasopressor agents); incorrect sensor application; highly calloused skin; or movement (such as shivering), especially during hypoperfusion.
To ensure accuracy, the sensor should return a steady pulse and/or pulse waveform. Pulse oximetry technologies differ in their abilities to provide accurate data during conditions of motion and low perfusion.